Georgia Tax Center (GTC) Guide: File, Taxes, & Deadlines
Are you prepared to navigate the complexities of Georgia's tax landscape, ensuring compliance and maximizing your financial well-being? Understanding Georgia's tax system is not just a civic duty; it's a crucial step towards securing your financial future and taking advantage of potential savings.
The Georgia Department of Revenue (DOR) offers a wealth of resources and information designed to help individuals and businesses alike. The primary portal for accessing these resources is the Georgia Tax Center (GTC), a secure and user-friendly platform that simplifies the process of managing your state tax obligations. Whether you're an individual filing your income tax return, a business owner managing sales and use tax, or a tax professional seeking guidance, the GTC provides a centralized location for all your tax-related needs.
To understand the Georgia tax system, it's essential to break down its key components. Georgia's individual income tax is primarily based on your federal adjusted gross income (AGI), the income you report before any deductions or credits. This AGI serves as the foundation for calculating your Georgia tax liability, subject to specific adjustments mandated by state law and your individual filing requirements. It's important to understand how these factors interact to determine your overall tax obligation.
Here's a detailed look at how Georgias state taxes work.
| Tax Type | Description | Key Features | Relevant Dates & Deadlines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Income Tax | Tax levied on an individual's income. |
|
|
| Sales and Use Tax | Tax on retail sales of tangible personal property and certain services. |
|
|
| Property Tax | Tax on the assessed value of real property. |
|
|
| Motor Fuel Tax | Tax on motor fuel, including gasoline and diesel. |
|
|
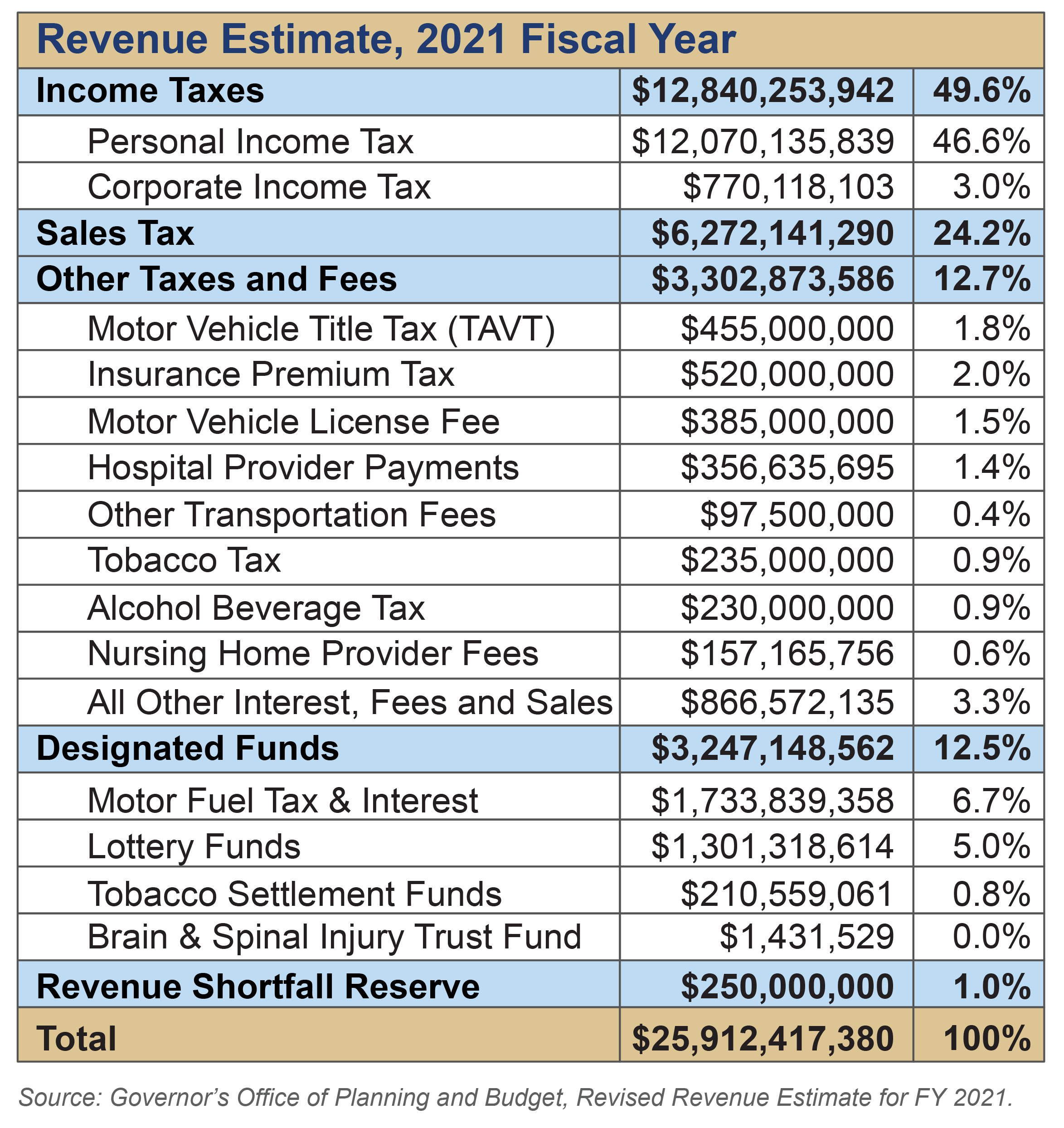
A significant change impacting Georgia taxpayers is the recent legislation, HB 111. This bill retroactively lowered the state income tax rate, starting January 1st. For the 2024 tax year (the return you file in 2025), Georgia has implemented a flat state income tax rate of 5.39%. This represents a considerable shift from the previous progressive tax system, where higher earners faced higher tax rates.
The implications of this shift are noteworthy. All taxpayers will now pay the same percentage of their taxable income, simplifying the tax calculation process. This change could potentially reduce tax burdens for some individuals while increasing them for others, depending on their income level and how it was previously taxed. This shift makes Georgia's state income tax system one of the most streamlined in the nation. As you prepare to file your 2024 tax return, this change will be reflected in your calculations, potentially impacting your tax liability or refund.
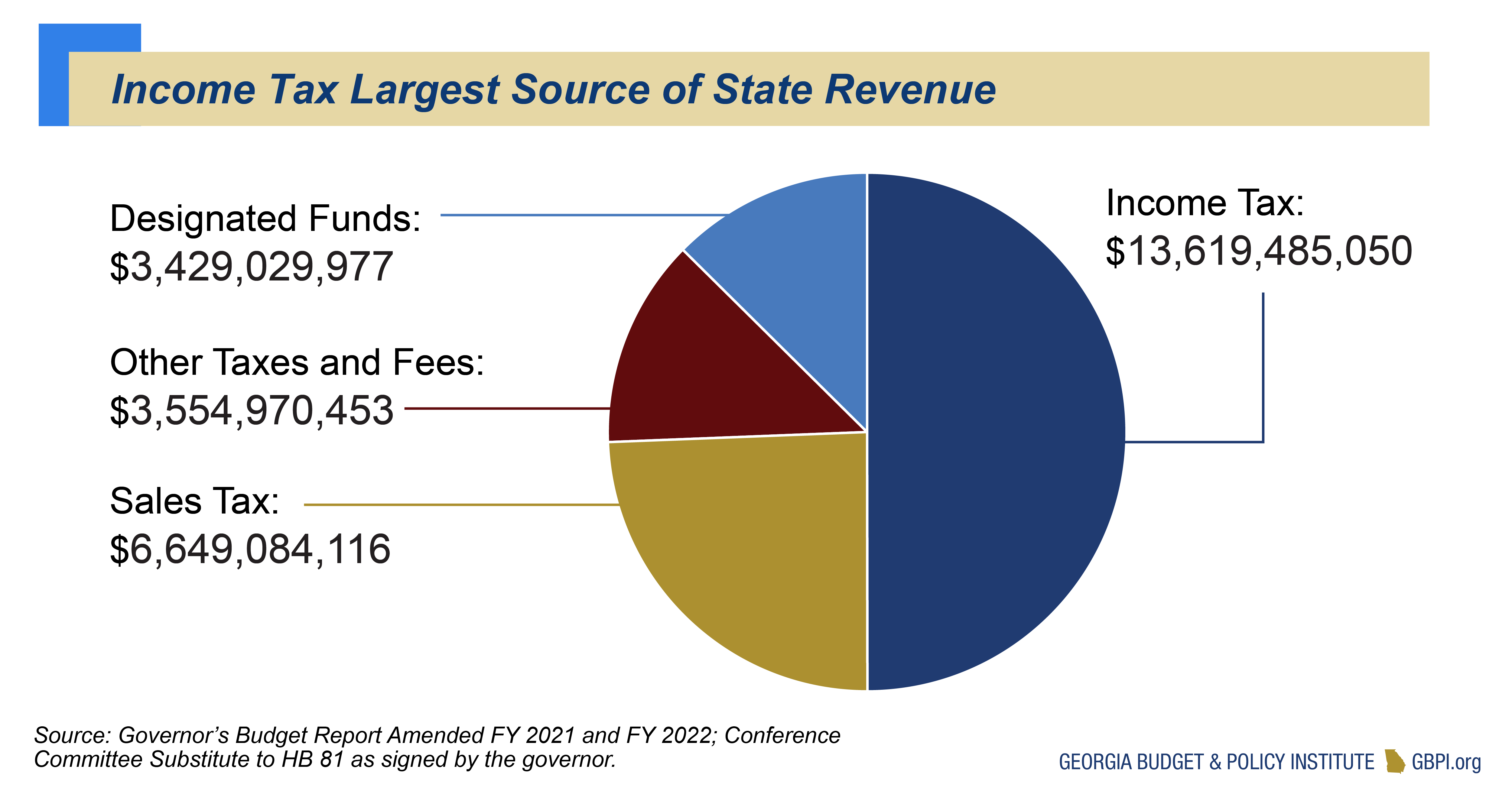
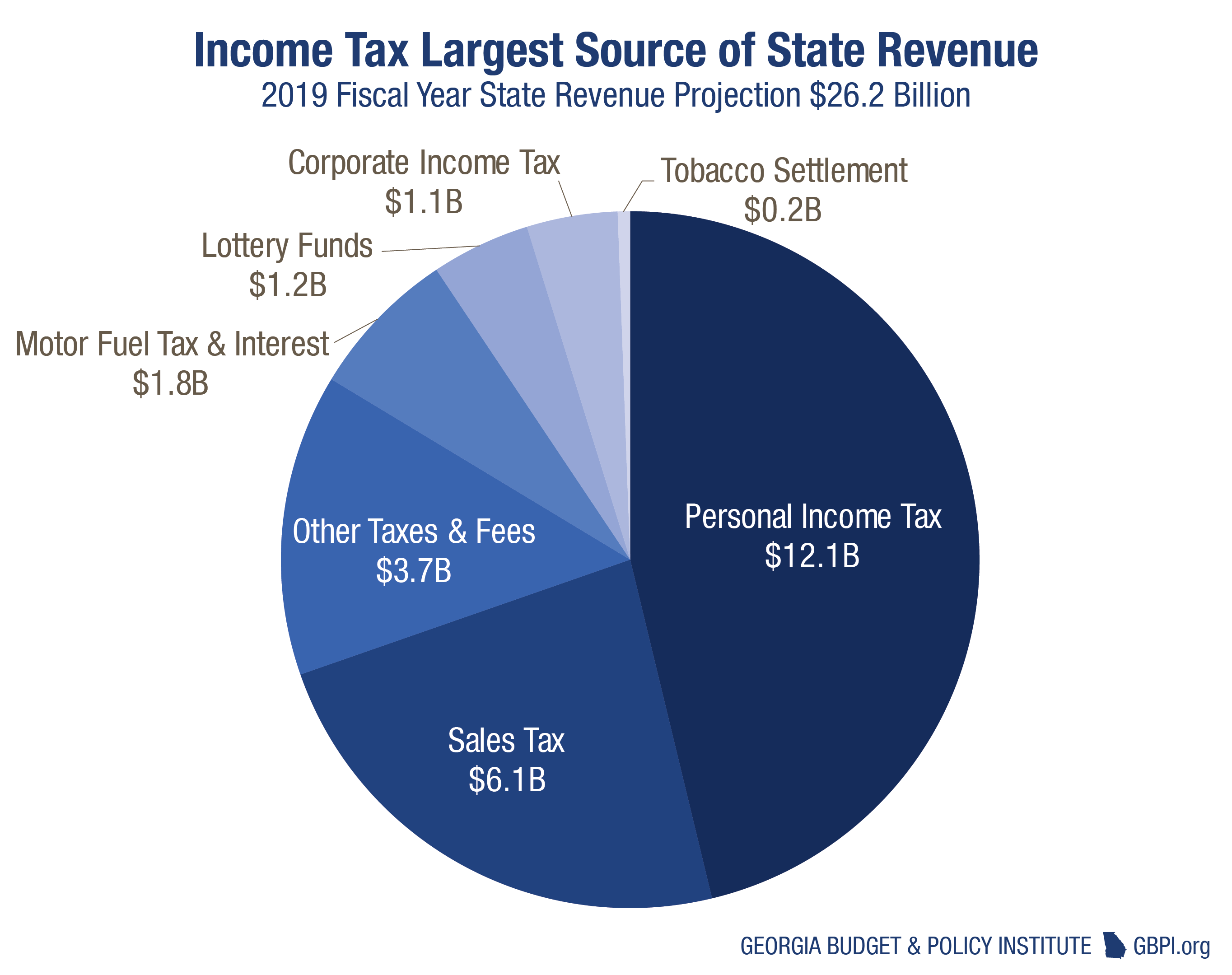
Beyond income tax, Georgia's tax system includes other crucial components, such as sales tax. Georgia imposes a state sales tax of 4% on most retail sales of tangible personal property and specific services. This tax affects both consumers and businesses, influencing purchasing decisions and impacting the overall cost of goods and services. It's important to understand the exemptions to sales tax to ensure you're not overpaying. These exemptions are defined under Georgia law (O.C.G.A.), so it's important to stay updated on current tax laws.
When it comes to real estate, property taxes are collected by local governments based on the assessed value of your property. The average tax rate in Georgia is around 0.72% of a home's assessed value, although this can vary significantly depending on the county and municipality. Homeowners should understand how property taxes are calculated in their specific area and stay informed about any changes to property assessments or tax rates.
Regarding deadlines, the due date for filing individual income tax returns for both 2023 and 2024 was May 1st. Those who requested an extension have until October to file their returns. It is important to file on time to avoid any penalties and also benefit from refunds. It's essential to keep track of these deadlines and file your returns accordingly, ensuring compliance with state regulations. The Georgia Department of Revenue typically begins processing 2024 individual income tax returns on Monday, February 3, 2025. Remember that most refunds are issued within three weeks from the date the return is received by the department.
As you navigate the tax process, remember the importance of security. The Georgia Tax Center (GTC) is designed to be a secure and accurate way to manage your state tax needs. Always ensure you're on an official state website before sharing sensitive or personal information. Look for the ".gov" suffix in the website address, and confirm that the email address ends with "georgia.gov" or "ga.gov". These indicators are a good way to verify the authenticity of the site.
The Georgia Department of Revenue (DOR) serves as the primary agency for tax collection and law enforcement in the state. The DOR offers a wealth of information for individuals, corporations, and tax professionals. You'll find answers to frequently asked questions, due dates, and other important tax-related details on the DOR website.
To facilitate payments, you can use the Georgia Tax Center (GTC). You'll need your Social Security number (SSN) or tax identification number (TIN) if you're paying without a GTC login. Payments can be made for the present tax year and back to 2007 for various tax types, including individual and corporate income tax, and liabilities issued by the DOR through assessment notices.
Here's a quick guide on how to approach tax-related matters in Georgia.
- Prepare Your Federal Return: Before starting your Georgia return, ensure your federal return is complete. This is the foundation for your Georgia income tax calculation.
- Visit the Georgia Tax Center (GTC): Go to the GTC website to access forms, instructions, and online services. This is the primary portal for all your tax-related needs.
- Gather Necessary Documentation: Collect all necessary documents, including your federal AGI, W-2 forms, 1099 forms, and any other documents relevant to your income, deductions, and credits.
- Calculate Your Georgia Tax Liability: Use your federal AGI, make any required adjustments as per Georgia law, and consider your filing requirements.
- Complete the Georgia Income Tax Return: Use the information from your federal return and the appropriate forms to complete your Georgia income tax return.
- File Your Return: Submit your return electronically through the GTC or by mail, following the instructions provided.
- Pay Taxes or Claim Refund: Determine if you owe taxes or are eligible for a refund. If you owe taxes, make your payment through the GTC or by other authorized methods.
Familiarize yourself with sales tax exemptions defined in the Official Code of Georgia Annotated (O.C.G.A.), and be aware of the prices and rates for calculating prepaid local tax on motor fuel, and state excise tax on motor fuel. Remember, you must pay state taxes as you earn or receive income during the year. Using the Georgia Tax Center (GTC) is the secure and recommended method for all your tax-related interactions.
In summary, navigating the Georgia tax landscape may seem daunting. However, with the help of resources and guidance from the Georgia Department of Revenue, you can ensure compliance and manage your financial obligations effectively. Embrace the GTC, understand your income, and stay informed about tax rates and rules. This proactive approach not only helps you fulfill your civic duties but also empowers you to make informed financial decisions and achieve your financial goals.
For accurate, secure, and up-to-date information, always refer to the official Georgia Department of Revenue website and use the Georgia Tax Center (GTC) for all your tax needs.