APA Citation Guide: Mastering Sources & Authors | Plus Tips!
Are you tired of wading through academic papers, unsure how to properly credit the sources that fuel your work? Mastering the art of citation isn't just about avoiding plagiarism; it's about building credibility and showing respect for the ideas of others.
The world of academia and professional writing thrives on the accurate and consistent citation of sources. Whether crafting a research paper, a journalistic piece, or a business report, knowing how to properly acknowledge the work of others is paramount. Proper citation ensures intellectual honesty and allows readers to trace the origins of information, verifying claims and exploring the topic further. This article will delve into the intricacies of citation, focusing on the APA (American Psychological Association) style, a widely used format, providing clear guidelines for a range of scenarios. We'll explore everything from citing single authors to navigating multiple authors, from handling page numbers to dealing with sources that lack a readily apparent author. Consider this your comprehensive guide to navigating the citation landscape, ensuring your work is not only well-researched but also ethically sound and professionally presented.
Lets begin with the basics. The core principle of citing sources, regardless of the specific style guide, remains consistent: to give credit where credit is due. In APA style, as in many others, citations serve two fundamental purposes: to acknowledge the source of information (be it an idea, a direct quote, or a paraphrase) and to provide readers with the necessary details to locate the original source.
Citations in APA style include two primary components: in-text citations and a comprehensive reference list at the end of the document. In-text citations appear within the body of your text and are typically enclosed in parentheses. The reference list provides complete bibliographic information for each source cited, allowing readers to easily find and consult the original materials. This two-part system ensures that the connection between your work and the sources you consulted is clear and unambiguous. To cite a source, the author's last name and the year of publication are included within the text. If a direct quote or a specific piece of information from a source is used, the page number(s) or other location identifiers (like chapter numbers, paragraph numbers, or section headings) are also included. For instance, a paraphrase from a 2020 article by Smith would be cited as (Smith, 2020), while a direct quote from page 45 would be cited as (Smith, 2020, p. 45).
Let's look at some common scenarios. If you are citing multiple sources by the same author within the same context, you can condense the in-text citation. For instance, if you are referencing work by Jones from 2018 and 2020, you can write (Jones, 2018, 2020). This is a clean and concise way to indicate that multiple works by the same author inform the current discussion.
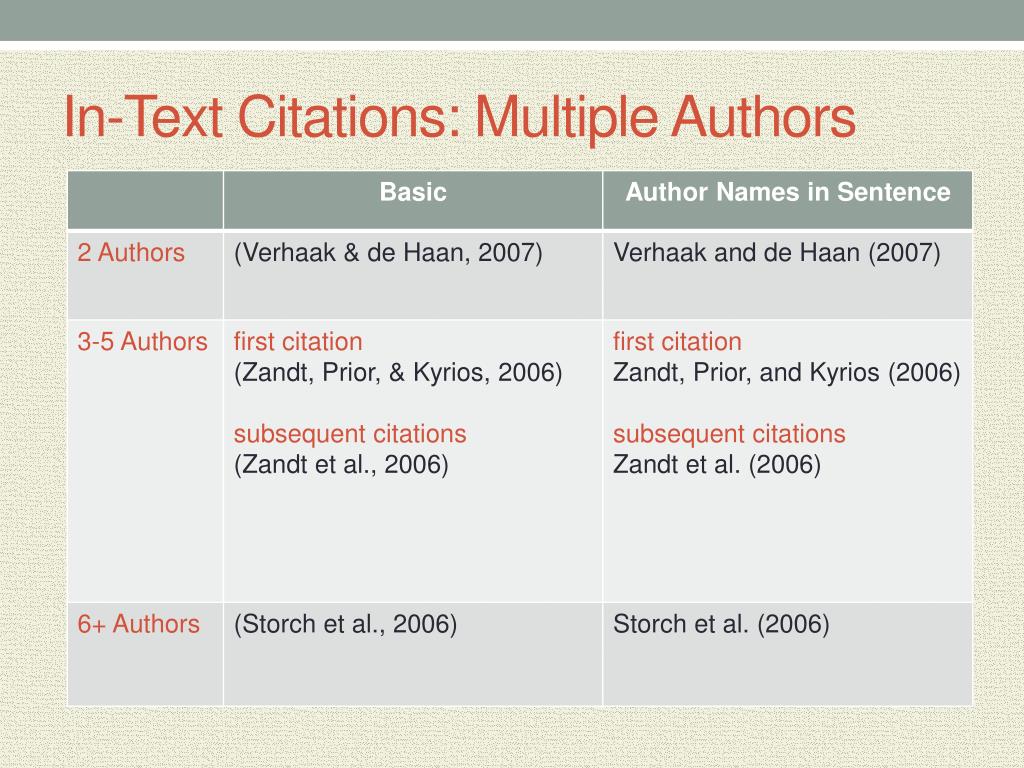
For two authors, the format is relatively straightforward. In the text, you always list both authors' names, separated by the word "and" within the text or with the ampersand (&) in parenthetical citations. For example, "Smith and Jones (2022) found that..." or "(Smith & Jones, 2022)." When it comes to three or more authors, the format becomes more streamlined. In the initial citation, you list all the authors' names. However, in subsequent citations, you use the first author's last name followed by "et al." (which is short for "et alii," meaning "and others") and the year. For example, if you are citing a work by Brown, Davis, and Miller (2021), your first in-text citation would include all three authors: (Brown, Davis, & Miller, 2021). Subsequent citations within the same paper would be (Brown et al., 2021).
In APA style citations, et al. is not italicized. Journal articles often list many authors, especially in the sciences. For works by two authors, list both in the reference list and the text (as in the Dittmar and Schemske example above). For three or more authors, list up to six in the reference list; For more than six authors, list the first three, followed by et al. (and others). When citing a source with two authors, include both authors' last names every time you cite the work. Use the ampersand (&) between the names. The authors designed a study to determine if social belonging can be encouraged among college students (Walton & Cohen, 2011). For three or more authors, include the last name of the first author, followed by et al. (not italicized), and the year.
What about the complexities of works with more than one author? Citing sources with multiple authors requires a slightly different approach. When a work has two authors, always cite both authors' names in your text: For works by two authors, list both in the reference list and the text (as in the Dittmar and Schemske example above). When citing a source that has two authors, you should separate their names with an ampersand in the parenthetical citation. For three or more authors, list up to six in the reference list; For more than six authors, list the first three, followed by et al. (and others).
When encountering sources without an author, the approach shifts. Movies, brochures, and website pages often do not have a visible author's name. In these instances, you typically cite the title of the work or the name of the organization responsible for it. If the source has no numbered divisions, cite only the year. If a source has no page numbers, you can use an alternative locator (e.g., chapter number, paragraph number, or section heading) or the name of the website or organization. The exact formatting will depend on the type of source and the information available.
When you use others' ideas (paraphrases) and direct quotes, you must cite your source by including the year of publication and, for direct quotes, the page number of the quote. Use 'p.' for a single page and 'pp.' for a page range: Meanwhile, another commentator asserts that the economy is 'on the downturn' (Singh, 2015, p. 23). To cite a source with multiple authors and an edition number in APA style, you need to know the names of the authors, title of the book, edition number, and publisher.
Citing sources with no author is another consideration. You can choose between two main options: parenthetical citations and numbered footnotes or endnotes. You should choose one of these two citation options and use it consistently throughout your text. You put your citations in parentheses within the text itself. It's common to come across sources without any authors. Movies, brochures, website pages often do not have a visible author's name. For more details on the reference list, please see reference examples.
For multiple works by the same author(s) in the same year, APA style provides a mechanism to differentiate them. Add a lowercase letter after the year for each source to distinguish between publications. For instance, if Smith published two articles in 2023, you would cite them as (Smith, 2023a) and (Smith, 2023b). The specific letter assigned is based on the order in which the sources appear in your reference list. The same principle applies to organization as author if an organization is the primary creator or publisher of the source.
Lets break it down step by step. Significant findings in a study of Los Angeles (McCroskey & O'Keefe, 2000). If you have two authors, use both authors' names in all citations. When you cite a source with two authors, you should separate their names with an ampersand in the parenthetical citation. The authors designed a study to determine if social belonging can be encouraged among college students (Walton & Cohen, 2011).
Including page numbers in citations is crucial for pinpointing the location of information, especially when using direct quotes or when referring to specific data or arguments within a source. Use 'p.' for a single page and 'pp.' for a page range: Meanwhile, another commentator asserts that the economy is 'on the downturn' (Singh, 2015, p. 23). Buford and Collins (2008) claimed that the meanings of words constantly change (p. 112).
To cite a source with an edition number in APA style, you need to know the names of the authors, the title of the book, the edition number, and the publisher. Use the edition number in your reference list entry. For example, if you are citing the second edition of a book, you would include "(2nd ed.)" after the title.
The two parts of citations in APA style include: (Authors Last Name, Year) and a complete reference should appear on your works cited page. Cite the year of the research publication in parenthesis right after you mention the author's name or right after a direct quote. The year of publication is crucial, providing temporal context. For direct quotes, the publication year and page number are necessary (only for direct quotes) - the page number of the quote.